About the Reedition of Phenster’s
In “Pandemonium Society House Rules,” L’avant garde #32, Phenster takes offense at the accusation that the Pandemonium Society plays an unsophisticated children’s game. As proof their D&D game is “plenty sophisticated,” he gives examples of the group’s house rules. Many more house rules follow in later issues of L’avant garde.
Phenster’s style, while explanative, is verbose and haphazard. My purpose in the reedition is only to make the rules more concise. Where I make assumptions or attempt to patch any holes Phenster leaves, I make it clear in the text.
Sources
In the August 1980 article, Phenster hints the starting point for the house rules is the Holmes edition of Basic D&D, which, once the perforated leaf is removed, has 46 pages. Later, he also writes that he started playing D&D when he got “a strange game that came in a box with a dragon on the top with 5 crazy dice” as a gift for Christmas in 1979.
He doesn’t specify the edition of Holmes. From the late date, we might assume 2nd or 3rd Edition. Other clues bear out the hunch. One article in the series adds a curious assortment of rules. Three entries among them come from the earliest printings of the D&D Basic Set:
Phenster adds an “enormous type to the spider list,” which has 6+6 hit dice. A new magic item is a “ring of plate mail,” and “Throwing salt on zombies makes them dry up and wither.”1
…[Phenster] started playing D&D when he got “a strange game that came in a box with a dragon on the top with 5 crazy dice” as a gift for Christmas in 1979.
That these are added as house rules further supports the idea that Phenster’s base rule set is not the 1st Edition (first three printings) of Holmes. The presence of only five dice in the box narrows the field to the fourth or fourth+ printings—both 2nd Edition, or the seventh, which is the last printing of Third Edition Holmes.2
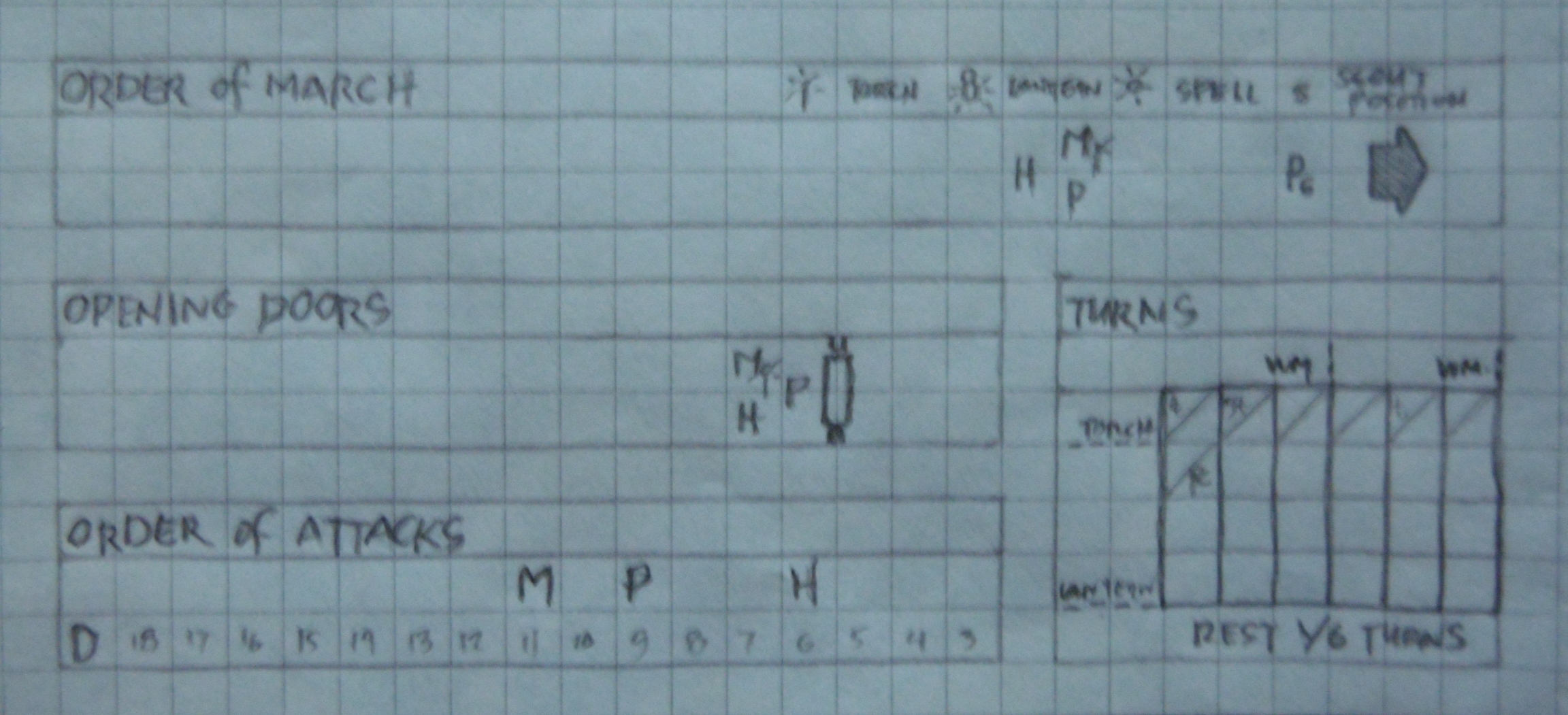
The dungeon Phenster mentions in his “Welcome” message in Paradigm Lost #1 (April 1980) is titled “The Great Halls of Pandemonium.” The name suggests there are multiple Great Halls, and the adventure locale described, “Great Crone Hall,” bears cosmetic resemblance to the Caves of Chaos from Dungeon Module B2. The dungeon consists of several rooms, densely populated by monsters. The accompanying narrative “dungeon report” indicates Great Crone Hall is higher up a cliff face from the previous dungeon and makes the conclusion “so it’s more dangerous.”
Similarities to the Caves end there. The map of Great Crone Hall shows the straight lines of stone-block construction, not natural or rough-hewn cavern walls. In the narrative, player characters 3rd-level and higher encounter monsters of up to 10 hit dice. Though when two player characters are felled and others wounded and short on spells, the party goes “back to the fortress to heal and get the gemstones appraised,” activities typically conducted in a base town.
But this only hints that Hazard, the DM who we presume made the dungeon, had some experience with The Keep on the Borderlands, which circulated by then in the sixth and seventh printings (November-December 1979) of the Holmes boxed set. I don’t know when the module became available separately in stores. In any case, the similarity does not mean B2 came in Phenster’s Christmas set.
…this only hints that Hazard, the DM who we presume made the dungeon, had some experience with The Keep on the Borderlands…
Although Phenster claims the single book in 1980, some additions and rules changes in articles from later years appear to be inspired from other sources. For examples: He makes specific reference to pole arm articles in the Strategic Review. He notes, in separate articles, that the Pandemonium Society uses the experience point tables for high level characters from Men & Magic and Greyhawk, and psionics from Eldritch Wizardry.
Categories
Phentster’s are a diverse array of house rules. He covers topics from the mundane cost of a sling, through the fantastic summoning of infernal beings, to the gonzo “rod of ICBMs.”
I class the house rules into the following four categories:
[H] Holmes
These house rules patch the Holmes edition to make it a more coherent game, while maintaining its simplicity. In this regard, Phenster does a decent darning job without sewing a whole new garment.
Examples: Damage and attacks per round by weapon class.
[E] Extra
Not strictly necessary, the rules in this category extend the game beyond 3rd character level and add elements that most gamers were used to even in the early ’80s. While these come with more complexity, they also add real value to the game without interfering with play.
Examples: Additional adjustments to ability scores, advancement to higher levels, wilderness exploration.
[C] Campaign
This category adds elements as suggestions or models to apply to a campaign. These ideas might be applied to a bare-bones campaign to give it some ambiance without much effort.
Examples: Coins of the realm, human languages, birds of war.
[P] Pandemonium
These are additional house rules employed by the Pandemonium Society. They often go a step—sometimes leagues—beyond fair or useful. But they can be fun.
Examples: Magic-use without spell books, combat complications, a number of improbable and horrific monsters, and “the Boomtown Rule.”
While Phenster’s start point is Holmes, many of the house rules are applicable to other old-school editions of the world’s most superlative role-playing game.
1 Again, Zach Howard’s Zenopus Archives cast light: in the Holmes first printing, an “enormous” 6-HD spider lurks in Room J (44), a ring of protection “serves as plate armor +1” (38), and zombies are vulnerable to salt (14).
2 See the Acaeum for an exhaustive list of D&D Basic Set contents by printings.



![Single Dice Roll [Traditional] Single Dice Roll [Traditional]](https://www.donjonlands.com/wp-content/uploads/_images/legacy/6a00d8342106f153ef02942f905f3b200c.jpg)